This content is password protected. You will find the password on my CV, or please contact me for access.
Author: Cormac Maher
Bookmarking App Interactive Prototype
High-Fidelity interactive prototype of a redesigned bookmarking system, this prototype, created using Marvel App, is part of a major research and design project I completed.
A/B Testing
A/B Testing
About
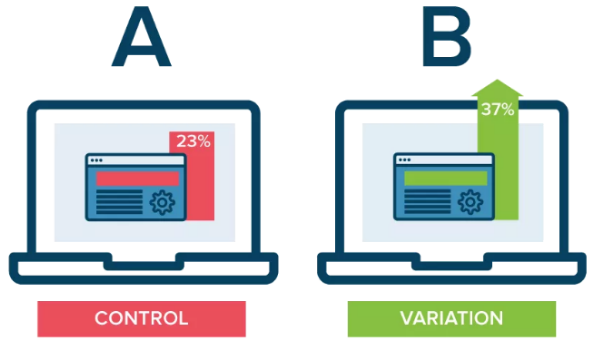
A/B testing is a form of quantitative user research, in which a control design is compared to a variety of slightly altered designs, to see which design is most effective in reaching the test goal.
Tests can be performed on most quantifiable metrics your site, including content, emails, and web forms.
A/B testing is also known as split testing, A/B/n testing, bucket testing, and split-run testing.
Read On >>A/B Testing
Tree Testing
Tree Testing
About
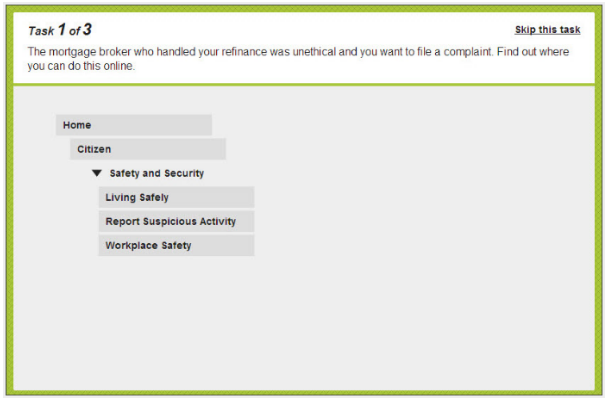
Tree testing is a research technique used on websites in order to understand the topic hierarchies a user perceives, and to evaluate content findability, with a goal of optimising that website’s information architecture (O’Brien D. 2009). It can be both a quantitative and qualitative method of research.
Read On >>Tree Testing
Diary Studies
About
Diary Studies are a type of qualitative longitudinal user research (Lallemand, C. 2012) used to record organic behavioural insights. Participants of diary studies self-report data about their experiences and activities, over a period of time. During this period participants will log data, collected in in a natural context, using a prescribed recording method. (Palen L., Salzman M. 2001)
Diary studies are also known as experience sampling or EMA (ecological momentary assessment) methodology (Wikipedia 2017, Experience sampling method.).
Read On >>Diary Studies
User Research Methods
This study explores a range of research methods that may be employed during a UX project. These methods may be used: at the beginning of a project to gain an understanding of the needs of the user and the tasks they need to perform; during a project to evaluate the current design iteration; and after a product has shipped to gain an understanding of how well it is performing relative to the product goals
Introduction
For this report three different methods of user research are being examined.
One method has been chosen from each of the three different phases of the product development lifecycle – Strategise, Execute and Assess.
Read On >>User Research Methods
7 – Evaluation
In order to uncover any usability problems in the UI, so that they can be addresed during the iterative design process, we undertake a stage of product evaluation using Nielsen’s Heuristics. These heuristics are a set of 10 user interface design guidelines applied to a UI, and evaluated by usability experts. Read On >>7 – Evaluation
6 – Paper Prototypes and Testing
As part of a formal testing process, we undertook testing our paper prototypes, and the goals and the scenarios we had developed.
The tasks we were testing were those identified, during the research stage, as the most popular features of the product. We would test for learnability, efficiency of use, errors and user satisfaction. Read On >>6 – Paper Prototypes and Testing
4 – Task Description
In order to better identify and understand the structure, flow, and the attributes of the tasks our app must facilitate, we must establish requirements. Read On >>4 – Task Description
3 – Personas
“Personas put a face on the user—a memorable, engaging, and actionable image that serves as a design target. They convey information about users to your product team in ways that other artifacts cannot.”
The Essential Persona Lifecycle – Your Guide to Building and Using Personas, Tamara Adlin and John Pruitt
Having already carried out our user survey, we were ready to create personas that were both assumption and data-based. Read On >>3 – Personas
2 – Research
Design research both inspires imagination and informs intuition through a variety of methods with related intents: to expose patterns underlying the rich reality of people’s behaviors and experiences, to explore reactions to probes and prototypes, and to shed light on the unknown through iterative hypothesis and experiment.
Jane Fulton Suri, creative director, IDEO – “Informing
Our Intuition: Design Research for Radical Innovation” – http://
bkaprt.com/jer/1/
Having chosen the audience engagement app as our project, we moved to the research stage. The purpose of this stage was to understand understand the needs of people for whom we were designing, the end users. The steps we would take were: Read On >>2 – Research
1 – Problem identification / Ideation
Human-Centered Design Project
Project Context, Background and Aim:
Identify a problem in an existing interface or choose an activity which has not yet been addressed by an app, website, etc. Carry out research to gain an understanding of the human and the tasks they need to perform. Based on this, design a paper prototype of an application, or part of an application, to better address the problem at hand.